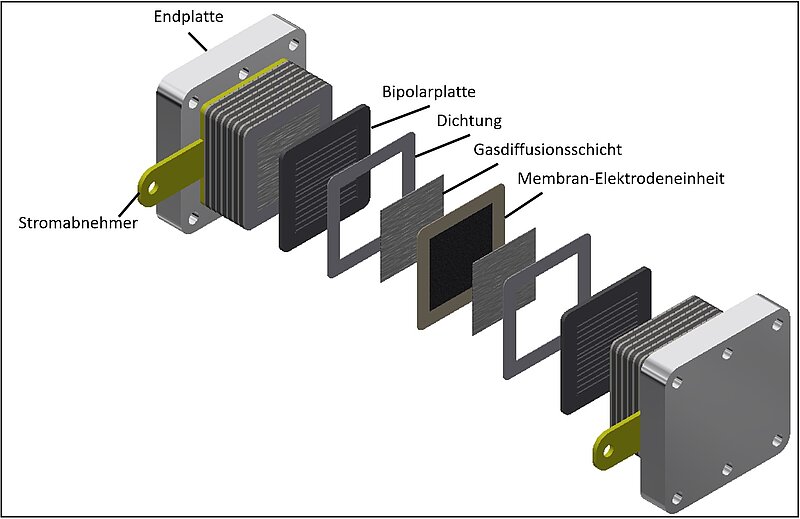
What are fuel cells?
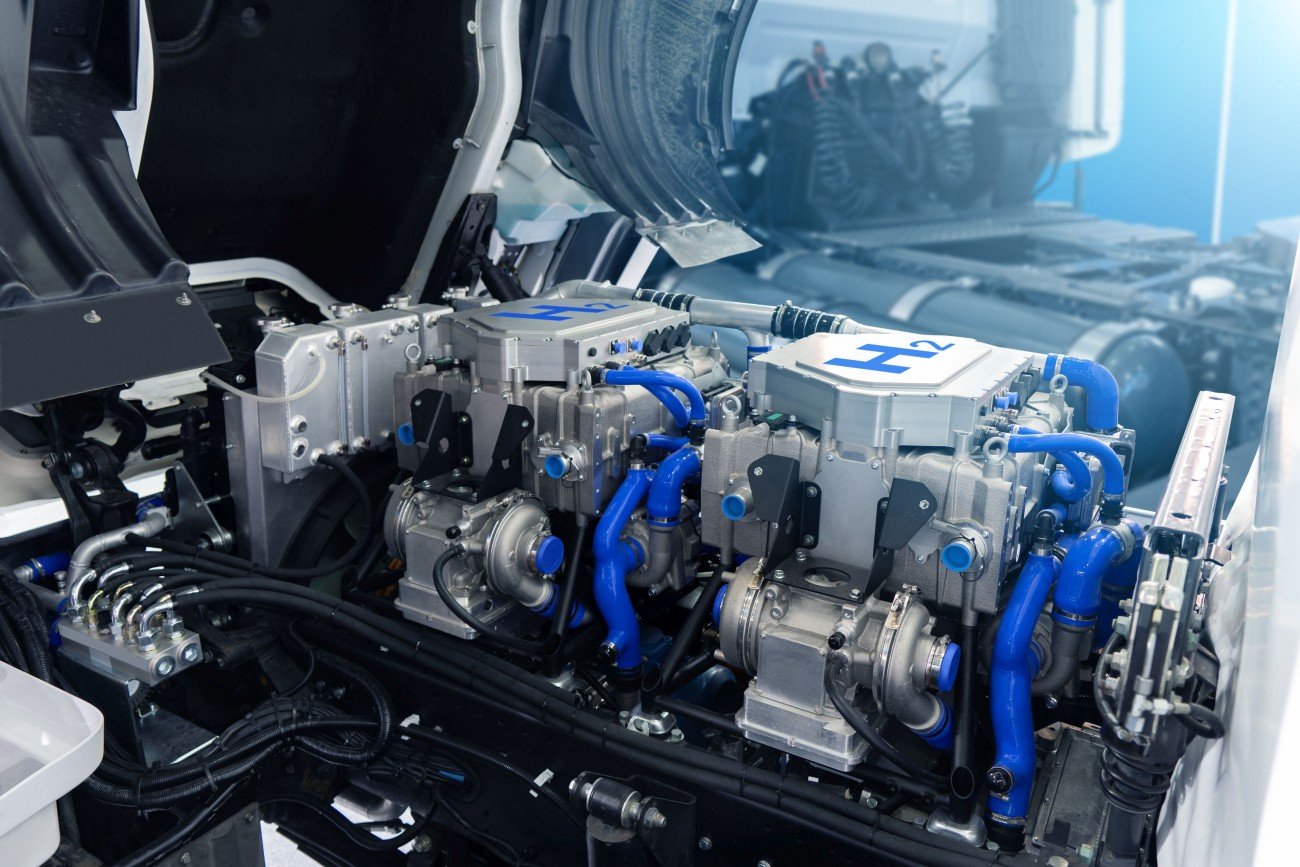
DILICO engineering's measurement technology has so far been used most for fuel cells. But what actually is a fuel cell? How does this technology work, what are the different types of fuel cells and where are they used? Which applications are already ready for the market and which still require further research and development work? You will find answers to these questions on this page. In addition, current research topics in the fuel cell sector are discussed and it is presented in which research projects DILICO eingineering is contributing its expertise and actively promoting the development of this technology.
The fuel cell is one of the hydrogen technologies and, like the redox flow battery or the electrolyzer, is an electrochemical energy converter. Through an electrochemical reaction, chemical energy is converted into electrical energy. This happens in the fuel cell through a so-called cold combustion. In this process, a fuel reacts with another chemical substance (usually oxygen or carbon dioxide) and generates an electrical voltage. The difference to hot combustion is that in cold combustion, the energy generated by the reaction or combustion is not transferred to another medium to generate electrical or kinetic energy.
The functioning principle of the fuel cell was already discovered in 1838 by the German Christian Friedrich Schönbein and the Briton William Robert Grove in 1839. However, since around the same time it was also discovered how to generate electricity with a generator, the principle of the fuel cell did not become established at that time.