The technology of the fuel cell is still new in today's application areas and requires test benches for continuous improvement, with which functionalities and operating strategies can be tested. Each of the different technologies of fuel cells and electrolyzers requires an adapted test environment. In the following, we will discuss the different types and their applications. Furthermore, we inform about the use of DiLiCo engineering's measurement systems in the context of test benches.
What is a test bench
A test bench is a device that can be used to test fuel cells or electrolysers reproducibly for their properties. These are equipped with extensive sensor technology and electrical controls in order to be able to image and record the behavior of the test object under investigation in a broad spectrum.
Currently, the hydrogen sector mainly uses development test benches. These require many and accurate sensors in order to analyze and optimize the measurement objects step by step, e.g. to achieve higher performance with the same use of resources.
Test benches can also be used for quality and functional testing of mass-produced products. The hydrogen technologies are currently in transition from semi-automated, to fully automated production. At this point, test stands are used for quality and functional testing. Depending on the application of the test bench, there are different demands on the sensor and measurement technology in the test benches.
Upcoming events with DiLiCo
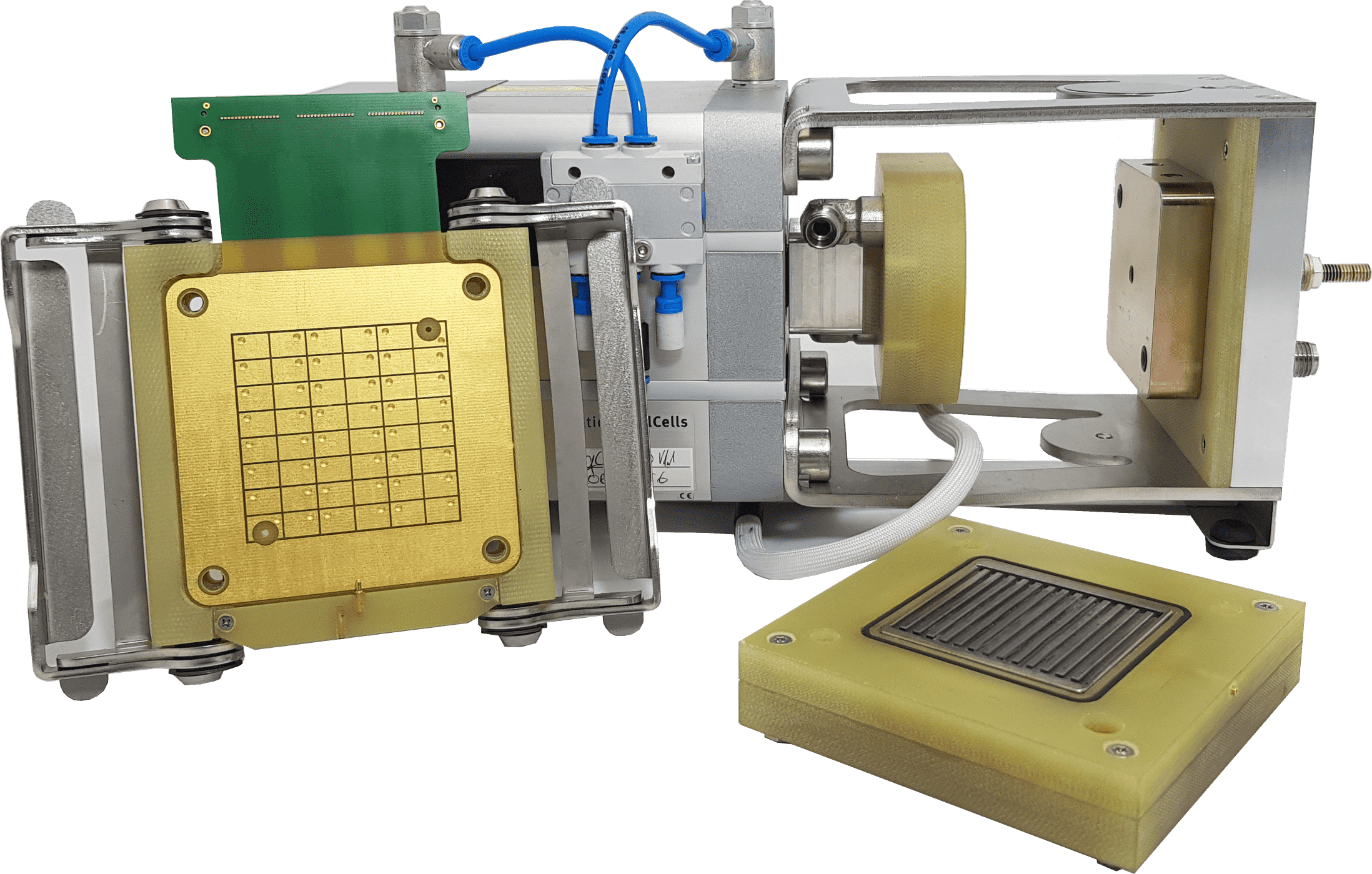
Image: The sensor layer of the meter DiLiCo current density for baltic qCf integriegt into the cell frame of the baltic quickCONNECT fixture.
Pneumatic test bench
In pneumatic test stands, compressed air is used to perform mechanical work. For the use of fuel cells and electrolyzers, there is an extra for these applications designed test bench for a single cell. The test stand qCf - quickCONNECT fixture is manufactured and sold by baltic FuelCells GmbH in Schwerin, Germany. The use of pneumatics in the test stand ensures continuous uniform pressure. Thus, complete reproducibility of the test conditions is ensured. This allows different components of a cell to be inspected and tested under exactly the same test conditions. The pneumatic test stand is available in different versions and is oriented to the size of the cell area, cooling and current intensity of the cells to be measured. The following versions are available:
- qCf FC 25 for a cell area of 25 cm²
- qCf FC 50 for a cell area of 50 cm²
- qCf LC high AMP for cells with very high currents and direct cooling
For more information on the test benches, visit the baltic FuelCells GmbH page.
DiLiCo current density for the baltic quickCONNECT fixture
For the special application area of the baltic test stand, DiLiCo has developed customized measurement technology that can only be used in the baltic qCf. For this purpose, an extra product series was designed for the DiLiCo current density measurement system, which adapts to the needs of the users. The DiLiCo current density product line for baltic qCf. Through this measurement system, the current density and temperature distribution in the cell can be measured and thus serves to accurately characterize the electrolytic cell or fuel cell..
Furthermore, the product series can measure especially high currents up to 6 A/cm². This has the advantage that with ever higher cell performance and the associated increase in current strength, the measurement system is excellently designed for the future.

Image: Pneumatic single-cell test stand from the company baltic FuelCells GmbH of Schwerin, Germany, with attached DiLiCo measurement technology for 25 cm² cell area.
Experimental test bench for reversible fuel cells
For the research field, especially in basic research, experimental test benches are used. These are primarily to ensure the basic functionality of the examined object. These experimental test beches are highly complex because many different parameters have to be monitored.
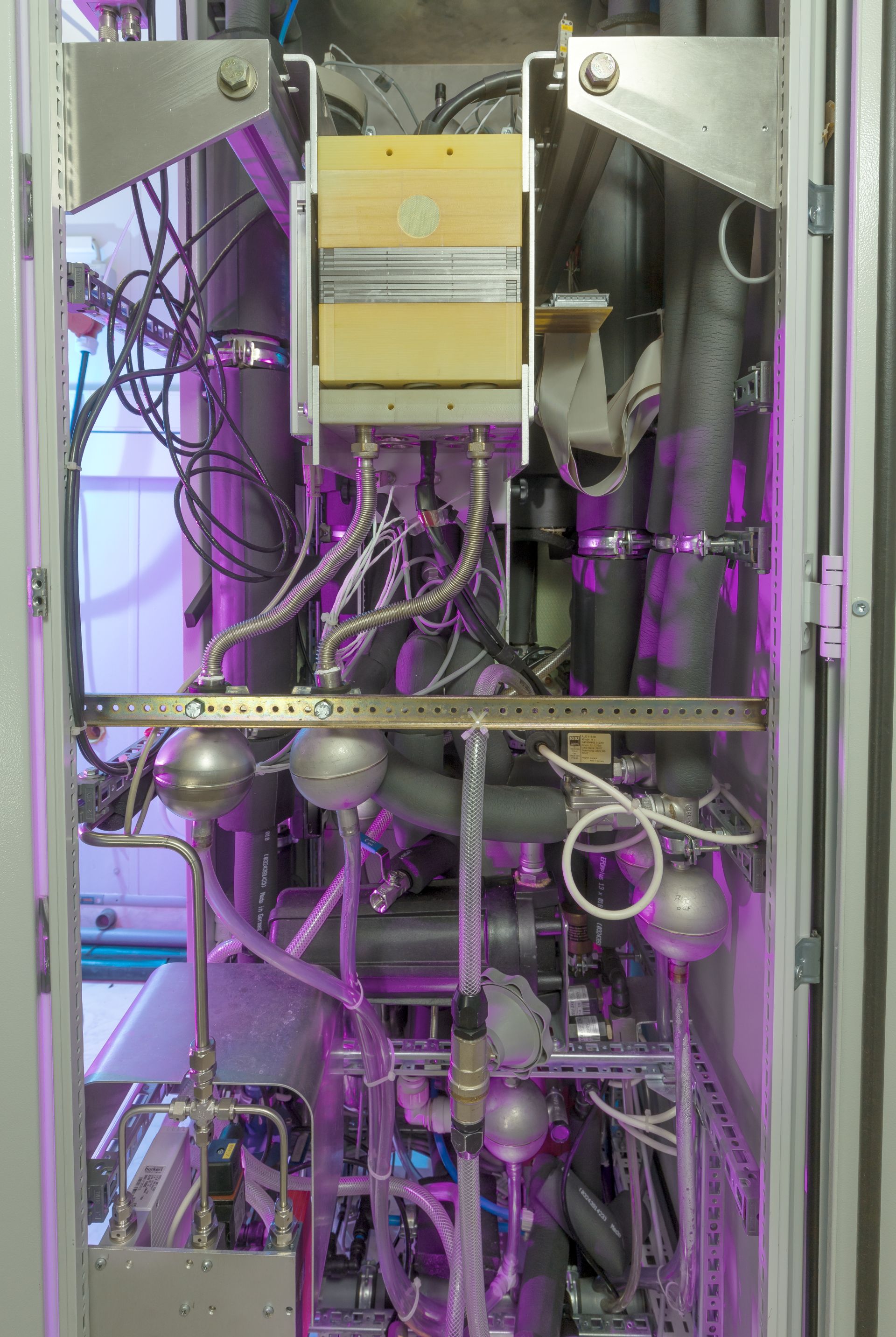
The picture shows a test stand for a reversible fuel cell. This can generate electricity from hydrogen as well as hydrogen from water. It unites the function of an electrolyser with that of a fuel cell in one stack. In the future, this can have considerable advantages in the scaling of such systems, since the peripheral components only have to be designed for one stack.
The test stand would be set up and put into operation as part of the RE-FLEX project at the University of Magdeburg. RE-FLEX is the acronym for "Unitary reversible PEM fuel cell for flexible energy storage".

Image: Experimental test bench for reversible fuel cells. Built by Philipp Kühne from DiLiCo and the inhouse engineering GmbH.
Test benches of our partner inhouse engineering GmbH
The test stands of our partner inhouse engineering GmbH from Berlin are specialized in the application for PEM technology. Thereby, test stands for single cells and for stacks can be offered individually to the customers' needs. Furthermore, the test stands can be selected between three temperature levels for the PEM technology:
- LT-PEM (Low temperature 30 – 80°C)
- MT-PEM (Medium temperature 30 – 120°C)
- HT-PEM (High temperature 120 – 180°C)
For more information on the test benches, service, control and software, visit the website of inhouse engineering GmbH.
DiLiCo measurement technologies for test benches
With its measurement technology in the field of single-cell voltage measurement, DiLiCo has set itself the goal of quickly and accurately acquiring and transmitting the measured values on the objects to be measured. Especially for development test benches, a very high measurement resolution is important. This is exactly where the DiLiCo cell voltage 48 and 96 product series come in. The version for measuring 48 or 96 cells stands out with the following advantages for use in test benches:
- Very fast measurement interval
- Very high measurement resolution
- Lowest measurement deviation
The meter contributes to the assessment of the entire system and also provides information on how quickly individual cells degrade..
Image: The fast and high resolution meter DiLiCo cell voltage 48 for single cell voltage measurement.
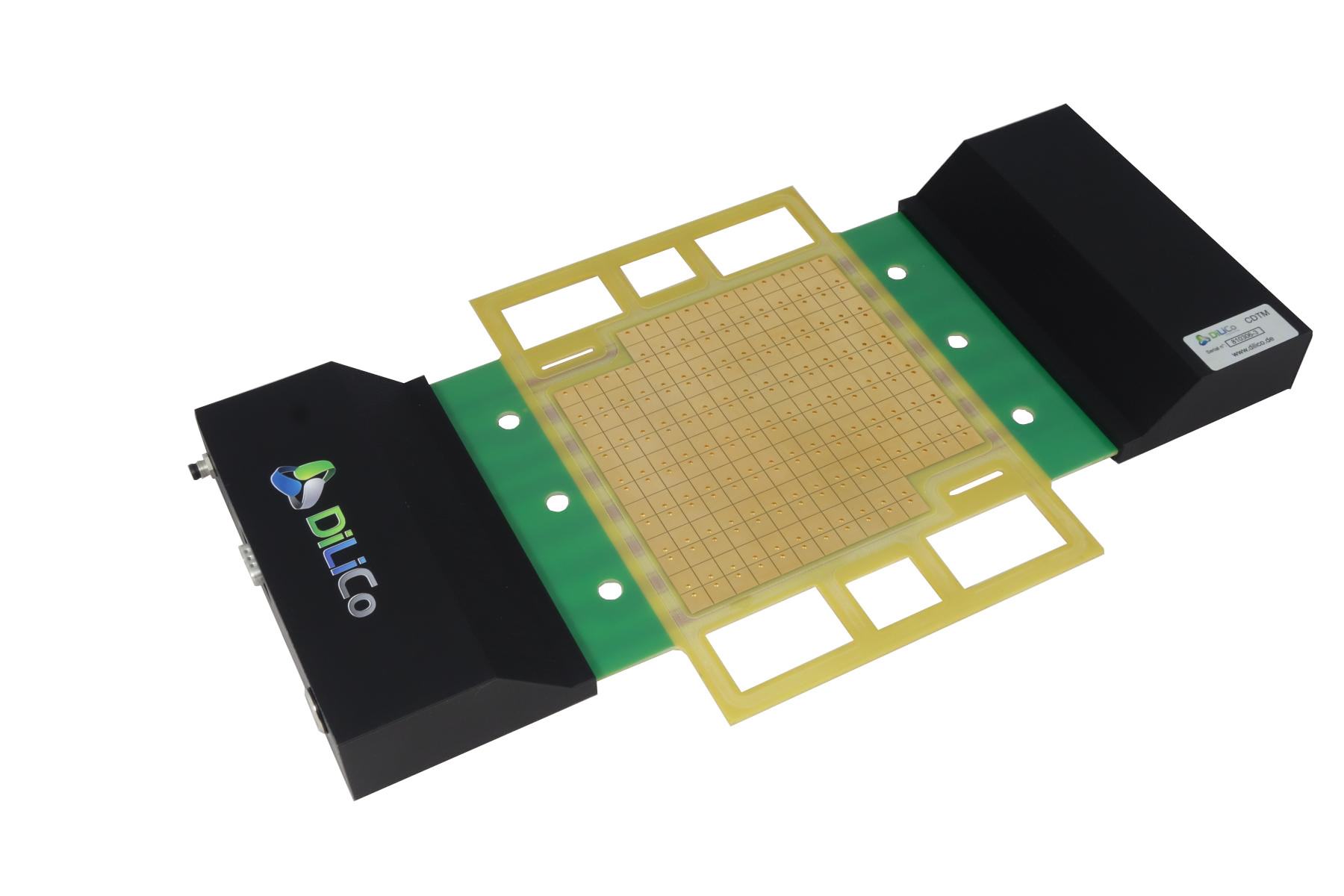
Image: The DiLiCo current density meter for measuring current density and temperature distribution during development.
Furthermore, DiLiCo not only develops and produces measurement systems for the baltic qCf, but also tailors them for other stack manufacturers. The DiLiCo current density product line offers exactly these solutions, which is perfectly designed for use in research and development test benches. The use of current density and temperature distribution measurement results in the following advantages for your test bench operation:
- Insights into local aging of the cell
- Insights into gas and reaction distribution
- Possible actions to increase efficiency
By using DiLiCo measurement technology, test benches in research and development can generate significant added value from the empirical values for operating strategies and for optimizing overall systems. Please feel free to contact us and we will advise you on your test bench project.
Where are test benches used?
Test stands for fuel cells and electrolysers are currently used a lot in research and development facilities. These include, for example, the Fraunhofer Institutes, universities and colleges, or the research and development departments of automotive manufacturers and suppliers. In the future, due to the widespread use of hydrogen in various sectors, many more users will be added.
What types of test stands are there?
There are basically two different types of test stands. The development test bench for development work of, for example, fuel cell systems, fuel cell stacks and also peripheral components and test benches for quality control and commissioning tests..
In the case of fuel cells and electrolysers, there are very different technologies, each of which has different framework conditions in terms of operating temperature, electrolyte or fuel. This also requires different types of test rigs. Test stands also differ in whether an entire stack or only a single cell is to be tested. Test stands for single cells are usually much smaller and more compact. The use of hydrogen in the test systems places further high safety requirements on the test rigs.
Test benches for fuel cells
Depending on the technology of the fuel cells, different requirements are placed on the functionality and components of a fuel cell test bench. A distinction can be made between a test bench for high-temperature fuel cells and a test bench for low-temperature fuel cells.
Test stands for high-temperature fuel cells in particular, such as the solid oxide (SOFC) fuel cell, which operates at temperatures of up to 600 °C, have a very special requirement for the robustness of sensor technology and peripheral components. In addition, fuel cell stacks vary significantly in size, i.e., the number of individual cells connected in series. This has effects on the applied voltage and current in the test system, which in turn has effects on the use of measurement technology for single cell voltage measurement in the test bench.
Test bench for electrolyzers
Electrolyzer technology is divided into different types of electrolyzers. Depending on the type of electrolyzer to be tested, there are different requirements for sensors and controls of the test stand. There are particularly large differences in the design of the electrolytic cell.
The test benches are precisely adapted to the type of electrolyzer. Thus, a change to another technology is seldom possible. In order to increase the degree of automation nevertheless, test rig manufacturers strive to cover as many technologies as possible with various products.

 Deutsch
Deutsch


